-
Problem based learning
普通类 -
- 支持
- 批判
- 提问
- 解释
- 补充
- 删除
-
-
Introduction
PBL IS A CONCEPT BORROWED from the medical field. It is an instructional strategy in which students, working in groups, take responsibility for solving real world problems. The instructor, instead of lecturing or leading a discussion, creates a hypothetical situation (problem) for the students and then takes a back seat as an observer and an advisor while the students work out a solution. Pertinent problems could be the creation of a energy conservation program or even the process of hiring a teacher (Bridges, 1992).

Most of the learning in PBL occurs within the context
of small groups rather than a traditional lecture.
-
Engagement
Students, individually and collectively, assume a major responsibility for their instruction and learning. "During the opening class periods of a unit, students explore the situation they have been given by building hypotheses that initiate investigation into the numerous aspects of the problem" (Stepien & Pyke, p. 381). Exploration is accomplished by activating students' prior knowledge, illustrating similarity of contexts in which information is learned, and later applied, and providing the opportunity for students to elaborate on that information.
-
Investigation and Inquiry
"During investigation and inquiry, students increase their knowledge and understanding of the concepts at work in their problem by consulting information resources and receiving appropriate amounts of direct instruction from their teacher" (Stepien & Pyke, p. 381). Instructors need to watch for students losing sight of the problem(s) and encourage them by providing opportunities for active responses, including them in various simulations, and offering immediate feedback.
PBL is beneficial because it can also can provide opportunities to create finished products. These created products optimize both retrieval memory and appropriate use of the knowledge that will be used in the students' future professional practices (Schmidt, 1983). For instance, in the future, PBL students learn to ask probing questions such as:What do we know? Who should do what?
What do we need to know? What did we find?
What resources can we use? What should we recommend?-
Outcomes When Using PBL
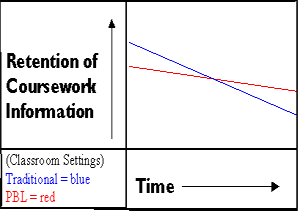
Across time, students retain less of what they learn
when taught in a traditional lecture format (Bok, 1989).
PBL students express positive attitudes and increased motivation toward their learning and adopt more desirable approaches to studying than students in traditional learning environments.
The tempo of student's work in a PBL environment more closely resembles the work of an administrator by often reevaluating circumstances after a change has been implemented.-
Conclusion
PBL is unlike a traditional learning environment where students usually occupy subordinate roles, spending most of their time receiving or observing information. Traditional students also rely heavily on the written mode of communication which often uses impersonal language and a detached style of learning. Furthermore, in the traditional learning environment, students work in a relatively placid emotional climate. Ideas, not feelings, are the currency of the realm.
The traditional learning environment and PBL are both conducive to learning, but it if an instructor can find a balance between theory (traditional) and practice (PBL) environments, learners will benefit more than ever before.-
Author
Produced by: Greg Cole, a Masters student in the Department of
Educational Technology at San Diego State University
Instructor: Bob Hoffman © 2001 -
-
- 标签:
- based
- traditional
- environment
- problem
- work
- students
- learning
- pbl
-
加入的知识群:



学习元评论 (0条)
聪明如你,不妨在这 发表你的看法与心得 ~